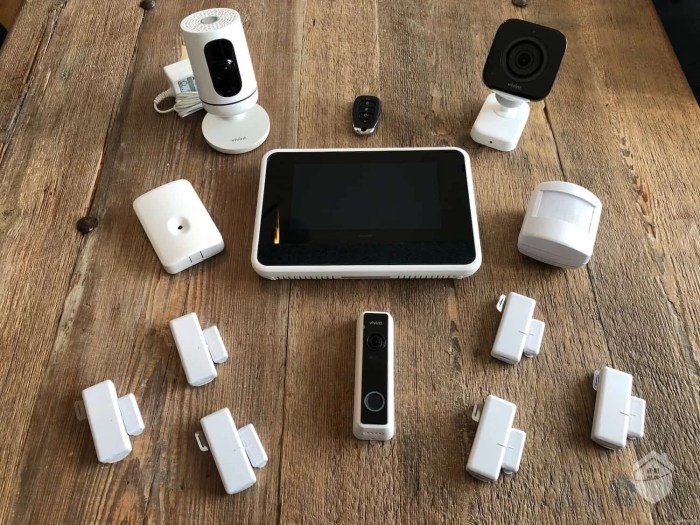
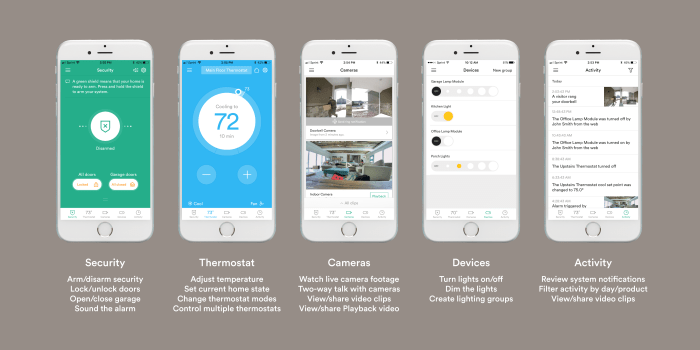
Business Security Systems Comprehensive Protection
Business security systems are paramount in today’s complex environment. From physical safeguards to robust cybersecurity measures, and encompassing data protection, a strong security posture is vital for any business. This comprehensive guide explores various aspects of these systems, including different approaches, practical examples, and the evolving landscape of threats and solutions.
The importance of comprehensive business security strategies extends beyond simply preventing breaches. Implementing effective systems creates a secure foundation for growth, reduces potential financial losses, and fosters trust with clients and employees. Understanding the diverse components of a robust security system, from physical access control to sophisticated data encryption, is crucial for modern businesses.
Introduction to Business Security Systems
Business security systems are no longer a luxury, but a necessity in today’s interconnected and often vulnerable digital landscape. Protecting sensitive data, physical assets, and reputation is paramount for any organization, large or small. Modern threats, ranging from sophisticated cyberattacks to physical property theft, demand proactive and robust security measures.
Effective business security systems encompass a multifaceted approach, covering physical protection, safeguarding digital assets, and implementing data protection strategies. This multifaceted approach ensures comprehensive security, mitigating risks across various potential vulnerabilities. By integrating preventative, reactive, and recovery strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the impact of incidents and maintain business continuity.
Types of Business Security Systems
A comprehensive security system for businesses requires careful consideration of various types of security. This includes both physical security, protecting the physical premises, and digital security, which safeguards the data and information systems. Data security is also crucial, focusing on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data.
- Physical Security: This involves measures to protect physical assets, such as buildings, equipment, and inventory. This encompasses aspects like access control systems, surveillance cameras, security personnel, and perimeter fencing. Physical security often involves a combination of these measures to deter potential threats and facilitate swift responses to incidents.
- Cybersecurity: This encompasses the protection of digital assets, including computer networks, software, and data. This includes measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and regular security audits. Robust cybersecurity practices are essential in today’s digital age to protect against cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Data Security: This involves protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This includes implementing encryption, access controls, data loss prevention (DLP) solutions, and regular data backups. Robust data security safeguards the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of crucial business information.
Benefits of Implementing Effective Business Security Systems
Implementing effective security systems offers a multitude of benefits, enhancing both operational efficiency and reputation. These benefits extend beyond simply avoiding financial losses.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Robust security systems can minimize downtime, reduce the frequency of incidents, and streamline incident response, ultimately leading to significant cost savings in the long run. For instance, a proactive security system can deter unauthorized access, reducing the need for extensive clean-up and restoration procedures after a breach.
- Enhanced Business Continuity: Implementing a comprehensive security system ensures the ability of the business to continue operating even during security incidents. This resilience safeguards critical business operations, prevents data loss, and reduces operational disruptions.
- Improved Customer Trust: Demonstrating a commitment to security fosters customer trust and confidence. Organizations with strong security measures can instill trust and reassure customers about the safety of their data and transactions.
Security Approaches for Businesses
A well-rounded security strategy encompasses various approaches, from proactive prevention to reactive measures and robust recovery plans.
- Preventative Strategies: These focus on mitigating risks before they materialize. This includes implementing security policies, conducting regular security assessments, and training employees on security best practices. A preventative approach often involves proactive measures such as security awareness training, strong passwords, and robust access controls.
- Reactive Strategies: These involve responses to security incidents. This includes incident response plans, incident management tools, and procedures for containing and resolving security breaches. A reactive approach is crucial for responding effectively to incidents when they occur.
- Recovery Strategies: These address the restoration of business operations after a security incident. This includes data recovery plans, business continuity plans, and disaster recovery plans. A well-defined recovery strategy minimizes the impact of incidents and allows for a swift return to normal operations.
Physical Security Systems
Physical security systems are crucial for protecting a business’s assets, personnel, and reputation. These systems act as the first line of defense against potential threats, deterring criminal activity and safeguarding valuable data and infrastructure. Robust physical security measures are essential for maintaining a safe and productive work environment.
Effective physical security goes beyond just installing alarms; it involves a comprehensive strategy tailored to the specific needs and vulnerabilities of each business. This approach considers factors like the business’s location, type of assets, and potential threats.
Types of Physical Security Measures
Various physical security measures contribute to a comprehensive security plan. These include deterrent measures like visible security personnel and well-lit areas, as well as active security technologies. These combined efforts can significantly reduce the risk of criminal activity and ensure business continuity.
- Alarms: These systems, ranging from simple intrusion alarms to sophisticated video-integrated systems, detect unauthorized entry or movement. They can trigger immediate alerts to security personnel, providing a rapid response to potential threats. A common example is the use of motion detectors in conjunction with audible alarms.
- Surveillance: Cameras, both fixed and mobile, are a vital component of modern physical security. They provide real-time monitoring of the premises, recording events for later review and potential legal use. This is particularly valuable in high-risk areas or for monitoring sensitive operations.
- Access Control: This encompasses systems that regulate who can enter and exit the premises, such as keypads, card readers, and biometric scanners. These systems provide a layer of security that prevents unauthorized personnel from gaining access to restricted areas. For example, controlled access is crucial in secure data centers or offices housing confidential information.
Examples of Effective Physical Security Systems
Effective physical security systems are adaptable to different business environments. The specific measures employed should align with the particular risks and vulnerabilities of the setting.
- Retail Stores: High-traffic retail locations often employ a combination of security cameras, motion detectors, and alarm systems. Access control measures may be utilized for staff entry and exit, and security personnel may patrol the premises. Well-lit parking lots and strategically placed security cameras contribute to deterring potential criminal activity.
- Warehouses: Warehouses, often storing valuable inventory, prioritize security measures that protect against theft and vandalism. Perimeter security, including fences, motion detectors, and lighting, is a key aspect. Internal surveillance and access control for employees are equally important.
- Office Buildings: Office buildings need systems that safeguard both personnel and sensitive data. Entry points are frequently equipped with security cameras and access control systems. Security guards and/or security patrols are often utilized, particularly in buildings with multiple floors or sensitive equipment.
Evaluating Physical Security Needs
A thorough assessment of physical security needs is critical for developing an effective security plan. This process considers the unique vulnerabilities and risks associated with a specific business.
- Identify Assets: This involves cataloging all valuable assets, including physical property, sensitive data, and important equipment. The value of each asset should be taken into account.
- Assess Threats: This stage entails identifying potential threats, including theft, vandalism, and acts of violence. Local crime statistics and past incidents can inform this assessment.
- Determine Vulnerabilities: Identifying weaknesses in the existing security infrastructure is crucial. This could involve weak points in the building’s structure or insufficient surveillance coverage.
- Select Appropriate Technologies: Based on the above steps, the right security technologies are chosen. This involves considering factors such as budget, technology availability, and the specific threats identified.
Comparison of Physical Security Technologies
A comparative analysis of different technologies provides insights into their strengths and limitations.
| Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Security Cameras | Real-time monitoring, deterrent effect, evidence collection | Potential for system failure, storage requirements, privacy concerns |
| Access Control Systems | Restricted access, enhanced security, audit trails | Cost of implementation, potential for system breaches |
| Alarm Systems | Immediate response to intrusion, deterrent effect | False alarms, reliance on response time |
Cybersecurity Systems
Protecting sensitive business data and infrastructure in today’s digital landscape is paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures are crucial for preventing breaches, maintaining operational continuity, and safeguarding reputation. Effective cybersecurity systems encompass various layers of protection, from network security to data encryption and user access controls.
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy addresses a range of potential threats, including malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches. Implementing and maintaining these systems requires ongoing vigilance, adaptation to evolving threats, and employee training to promote a security-conscious culture.
Common Cybersecurity Measures
Implementing various cybersecurity measures is essential for mitigating risks and protecting sensitive information. These measures act as a layered defense against potential threats. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-virus software are key components in this layered approach.
- Firewalls act as a gatekeeper, controlling network traffic and preventing unauthorized access. They monitor incoming and outgoing data packets, blocking malicious traffic while allowing legitimate communication. Sophisticated firewalls often employ rules-based systems, allowing administrators to define specific traffic patterns to permit or deny.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are designed to detect and alert on suspicious activity within a network. They constantly monitor network traffic for patterns indicative of attacks, such as unusual login attempts or unauthorized access attempts. IDS systems often use signature-based detection, identifying known malicious patterns, and anomaly-based detection, flagging unusual or unexpected activity.
- Anti-virus Software is essential for protecting individual computers and servers from malware. It scans files and applications for known malicious code, quarantining or deleting threats. Modern anti-virus solutions often include real-time scanning, proactive protection against zero-day threats, and cloud-based threat intelligence to stay ahead of evolving malware.
Common Cybersecurity Threats
Businesses face a variety of evolving cyber threats. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective security strategies. These threats can range from sophisticated attacks targeting sensitive data to simpler but potentially damaging phishing scams.
- Malware, including viruses, worms, and Trojans, can disrupt operations, steal data, or damage systems. These malicious programs can be disguised as legitimate software, making them difficult to detect. Sophisticated malware often employs techniques like polymorphic code to evade detection.
- Phishing Attacks involve tricking users into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or credit card details. These attacks often leverage social engineering tactics, impersonating trusted entities or exploiting user anxieties.
- Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands payment for its release. Ransomware attacks can severely disrupt business operations and lead to significant financial losses.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks flood a network or system with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. DoS attacks can cripple business operations, preventing access to essential services and applications.
Creating a Strong Cybersecurity Policy
A robust cybersecurity policy is a cornerstone of a strong security posture. It Artikels the rules and procedures for protecting company data and systems. This policy should be easily understood and consistently enforced.
- A well-defined cybersecurity policy should establish clear responsibilities for individuals and teams. This ensures accountability and promotes a security-conscious culture.
- The policy should cover access controls, data encryption, password management, and incident response procedures. Regular reviews and updates are essential to address evolving threats.
- Regular security awareness training for employees is vital. This helps to educate them about common threats and best practices for protecting company data.
Best Practices for Securing Business Networks and Data
Implementing best practices significantly enhances security posture. Proactive measures are more effective than reactive responses.
- Regular Software Updates: Applying security patches and updates is essential for closing vulnerabilities in software applications and operating systems. This reduces the risk of known exploits and vulnerabilities.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforcing strong and unique passwords for all accounts is vital. Password managers and multi-factor authentication can significantly enhance security.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implementing regular data backups ensures business continuity in case of data loss or system failure. Proper disaster recovery planning is crucial for restoring operations quickly.
Cybersecurity Threats and Impact
Understanding the impact of different threats is crucial for prioritization and mitigation. The table below illustrates various cybersecurity threats and their potential consequences.
| Threat | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Malware | Malicious software designed to damage or disrupt systems | Data loss, system disruption, financial loss, reputational damage |
| Phishing | Deceptive emails or messages attempting to gain sensitive information | Data breaches, financial fraud, compromised accounts |
| Ransomware | Malicious software that encrypts data and demands payment for its release | Data loss, operational disruption, financial extortion |
| DoS | Attack that floods a system with traffic, rendering it unavailable | Service disruption, lost revenue, reputational damage |
Data Security Systems
Data security is paramount in today’s interconnected business world. Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction is crucial for maintaining trust, complying with regulations, and safeguarding a company’s reputation. A robust data security system is no longer a luxury but a necessity for sustainable growth and operational efficiency.
Data breaches can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Implementing comprehensive data security measures is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure business continuity. These measures encompass a range of strategies, from encryption and access controls to robust backup and recovery procedures.
Importance of Data Security in Modern Business
Data security is critical for maintaining a company’s reputation and customer trust. A strong security posture demonstrates a commitment to protecting sensitive information, fostering customer confidence, and minimizing the potential for financial and operational disruptions. Furthermore, data security is vital for regulatory compliance and avoiding potential legal repercussions.
Data Security Measures
A multifaceted approach to data security is vital. These measures include robust encryption techniques, stringent access controls, and reliable data backup and recovery strategies.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest protects it from unauthorized access. This involves using strong algorithms and keys to scramble data, rendering it unintelligible to unauthorized parties. For example, HTTPS encrypts web traffic, while database encryption protects data stored in databases.
- Access Controls: Implementing strict access controls defines who can access specific data and under what conditions. This involves using user authentication, authorization mechanisms, and role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to only authorized personnel.
- Data Backups: Regular data backups are essential for disaster recovery. These backups safeguard against data loss due to hardware failures, cyberattacks, or human error. Different backup strategies, including full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups, cater to varying needs and recovery time objectives (RTOs).
Comparison of Data Security Solutions
Different data security solutions cater to specific needs and budgets. Choosing the right solution requires a careful evaluation of their strengths and weaknesses.
- Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and cost-effectiveness but may introduce security risks if not properly managed. Security measures should be taken to protect cloud-based data. Robust cloud security solutions, like encryption at rest and in transit, along with strong access controls, are critical.
- On-premises solutions provide greater control over data security but often involve higher upfront costs and require dedicated IT infrastructure.
- Hybrid solutions combine the benefits of cloud and on-premises solutions, allowing businesses to tailor their data security strategy to their unique needs.
Developing a Comprehensive Data Security Plan
A comprehensive data security plan involves a systematic approach to risk assessment, policy development, and implementation. A well-defined plan Artikels specific measures for preventing and responding to security threats.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities in the data security system, assessing their likelihood and potential impact.
- Policy Development: Establish clear policies and procedures for data security, outlining responsibilities and expectations for all employees.
- Implementation: Implement the chosen security measures, ensuring compliance with established policies and procedures.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the data security plan, identifying areas for improvement and adapting to evolving threats.
Data Security Policies for Different Departments
Different business departments require tailored data security policies to address their specific needs and responsibilities.
| Department | Data Security Policies |
|---|---|
| Sales | Restrict access to customer data based on roles and responsibilities; implement data encryption for customer information; enforce secure password policies. |
| Finance | Implement multi-factor authentication for financial transactions; encrypt financial data both in transit and at rest; secure access to financial records based on roles and responsibilities. |
| Human Resources | Implement access controls for employee data, ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive information; encrypt sensitive data like salary information. |
Integration and Management of Security Systems

Source: fedsecurity.com
Effective integration of diverse security systems is crucial for a comprehensive security posture. A siloed approach, where individual systems operate independently, can create vulnerabilities. Integrating these systems allows for a unified view of threats and facilitates a more coordinated response. This holistic approach enhances the overall security posture, optimizing resource utilization and enabling a faster, more effective reaction to security incidents.
Effective Integration of Security Systems
Integrating various security systems demands careful planning and execution. A key aspect is ensuring compatibility between different hardware and software components. This includes selecting systems with open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow for seamless data exchange. A thorough assessment of existing infrastructure and potential compatibility issues is essential. Careful consideration must be given to the communication protocols and data formats utilized by the various systems. A well-defined data exchange strategy, including security protocols for transmission, is vital for a seamless integration.
Importance of System Management and Monitoring
Proactive system management and continuous monitoring are fundamental to maintaining optimal security. This involves employing robust monitoring tools to track system performance, identify anomalies, and proactively address potential issues. Centralized management platforms consolidate data from various security systems, offering a unified view of security events and enabling rapid incident response. Regularly scheduled system maintenance tasks and security patching procedures, performed by qualified personnel, are essential to mitigate vulnerabilities and maintain optimal system performance.
Methods for Conducting Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security audits and assessments are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in security systems. Penetration testing methodologies simulate real-world attacks to assess the system’s resilience. Vulnerability scanning tools identify known security flaws within the infrastructure, providing a proactive means to address weaknesses. Thorough security audits and assessments should encompass all aspects of the security systems, from physical access controls to network configurations. These assessments should also include a review of security policies and procedures to ensure alignment with best practices.
Step-by-Step Guide for Maintaining and Updating Security Systems
Maintaining and updating security systems requires a structured approach. This includes regular software updates to address known vulnerabilities. A documented maintenance schedule should be in place to ensure timely updates and preventative maintenance. Regular system backups, ensuring data integrity and recovery capabilities, are vital. The process should also involve employee training on security protocols, and routine security awareness programs to educate personnel about potential threats and best practices.
Security System Maintenance Schedule
A well-structured maintenance schedule is crucial for optimal system performance and security. This schedule should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changing security needs. The following table Artikels a suggested security system maintenance schedule, adaptable to specific business requirements.
| Task | Frequency | Responsible Party | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Updates | Monthly | IT Department | Apply security patches and updates to all security systems. |
| System Backups | Weekly | IT Department | Create full backups of all critical data and systems. |
| Vulnerability Scanning | Quarterly | Security Team | Identify and remediate security vulnerabilities. |
| Penetration Testing | Semi-annually | External Security Consultant | Simulate real-world attacks to evaluate system resilience. |
| Security Policy Review | Annually | Security Team | Ensure policies align with best practices and evolving threats. |
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Security Systems

Source: stingalarm.com
A crucial aspect of implementing any security system is a thorough cost-benefit analysis. This analysis helps businesses determine if the investment in security measures is justified by the potential return on investment (ROI). A well-executed analysis ensures that security spending aligns with overall business objectives and prioritizes the most impactful solutions.
A sound cost-benefit analysis allows businesses to allocate resources effectively, selecting security solutions that provide the best possible protection at the most favorable cost. This careful consideration ensures that security investments contribute positively to the bottom line.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Security Systems
Various factors influence the price of security systems. These factors range from the sophistication of the technology to the scale of the business and its specific security needs.
- Technology Complexity: Sophisticated security systems with advanced features, such as real-time video surveillance with AI-powered analytics, tend to be more expensive than basic systems. For example, a sophisticated access control system integrating biometric authentication will likely cost more than a system relying solely on PIN codes.
- Scalability: The size of the protected area and the number of assets or personnel to be secured directly impacts the cost. A larger business or organization with extensive facilities will need a more comprehensive and scalable security system, resulting in higher initial and ongoing costs.
- Integration Requirements: Integrating existing security systems with new ones can increase costs. The complexity of integration with other business software, such as accounting or customer relationship management (CRM) systems, can significantly affect the price.
- Maintenance and Support: Ongoing maintenance, including software updates, repairs, and professional support, contributes to the overall cost of ownership. Systems requiring frequent maintenance or specialized expertise will have higher ongoing costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industry-specific regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare or PCI DSS for financial institutions, can dictate the required security measures, leading to increased costs.
Potential Return on Investment (ROI)
The ROI of a security system is not always immediately apparent. However, the benefits extend beyond immediate cost savings.
The primary benefits of security systems often involve preventing or minimizing financial losses, such as theft, fraud, or damage. These benefits can be significant. For example, a well-implemented security system can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, which could lead to substantial financial penalties or reputational damage.
Methods for Assessing Cost-Effectiveness
Several methods exist to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of different security solutions. A key method is comparing the cost of each solution with the potential risk reduction it provides.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This involves meticulously quantifying the potential benefits of a security system, including reduced losses, improved efficiency, and enhanced reputation. The cost of implementing and maintaining the system is weighed against these potential benefits to determine the overall cost-effectiveness.
- Risk Assessment: Understanding the specific security risks a business faces is essential. This helps prioritize the most critical security vulnerabilities and tailor security solutions to address those vulnerabilities. A comprehensive risk assessment can guide the selection of the most effective security solutions.
- Scenario Planning: Examining potential security breaches or incidents and calculating the potential financial impact can help justify the cost of a security system. By anticipating potential risks, businesses can better estimate the value of the security system in preventing or mitigating those risks.
Case Study: ABC Company, Business security systems
ABC Company, a retail chain, experienced significant losses due to shoplifting. They implemented a comprehensive security system, including advanced surveillance and access control. Within six months, the shoplifting incidents reduced by 40%, directly translating into substantial cost savings. The return on investment was achieved not only through decreased losses but also through improved staff morale and increased customer confidence.
Comparison of Security System Solutions
| Security System | Initial Cost | Maintenance Cost | Potential ROI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Surveillance System | $5,000 | $1,000/year | Reduced shoplifting by 10%, preventing $10,000 in losses |
| Advanced Surveillance System with AI | $15,000 | $2,000/year | Reduced shoplifting by 40%, preventing $40,000 in losses |
| Biometric Access Control System | $10,000 | $500/year | Reduced unauthorized access by 25%, preventing $5,000 in losses |
Emerging Trends in Business Security
Modern businesses face a constantly evolving threat landscape. Staying ahead of these threats requires understanding and adapting to emerging trends, particularly those involving artificial intelligence and machine learning. Proactive security measures are critical to mitigating risks and safeguarding valuable assets.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Security
AI and machine learning are rapidly transforming security systems. These technologies enable businesses to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate security breaches. This capability allows for proactive threat detection and response, significantly enhancing security posture.
Examples of AI and ML in Security
Numerous applications leverage AI and machine learning for enhanced security. For instance, AI-powered intrusion detection systems can identify suspicious network activity by analyzing traffic patterns and user behavior. Machine learning algorithms can also analyze data from security cameras and other sensors to identify potential threats in real-time, significantly improving threat detection accuracy. Furthermore, AI-driven fraud detection systems can identify fraudulent transactions by recognizing patterns and anomalies in financial data.
Future Implications of Emerging Trends
The integration of AI and machine learning into security systems will reshape the future of business security. Businesses will be able to respond more quickly to threats, reducing the impact of security incidents. AI-powered systems will automate many security tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic initiatives. This shift towards proactive and intelligent security will necessitate a change in security professionals’ skillsets.
Importance of Staying Informed
The security landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats and solutions emerging frequently. Staying informed about the latest developments in security is crucial for businesses to maintain a robust security posture. Regular updates on emerging threats and technologies will be critical for protecting against new vulnerabilities. Continuous learning and adaptation to these advancements are essential to maintaining a secure environment.
Potential Impact of Emerging Security Technologies
| Technology | Potential Impact | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered Intrusion Detection Systems | Increased detection accuracy, proactive threat response, reduced false positives. | Analyzing network traffic patterns to identify malicious activity before it causes damage. |
| Machine Learning-Based Fraud Detection | Reduced financial losses, improved transaction security, increased operational efficiency. | Identifying fraudulent transactions in real-time, preventing financial losses, and minimizing operational disruptions. |
| AI-driven Threat Intelligence Platforms | Proactive threat hunting, enhanced threat response capabilities, improved threat prioritization. | Analyzing threat data from multiple sources to provide actionable intelligence about potential threats, enabling proactive security measures. |
| Autonomous Security Systems | Reduced reliance on human intervention, improved response time, 24/7 security monitoring. | Systems automatically responding to threats, initiating security measures, and minimizing downtime. |
Illustrative Examples of Security Systems

Source: gossiboocrew.com
A robust security system is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses across various sectors. Illustrative examples demonstrate how tailored security measures can mitigate risks and safeguard valuable assets, from sensitive data to physical infrastructure. These examples highlight practical applications, showing how different security systems complement each other to create a comprehensive defense strategy.
Security Systems in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations handle sensitive patient data, demanding stringent security measures. Implementing multi-layered security systems is crucial. Physical security systems, such as controlled access points and surveillance cameras, are essential to protect facilities from unauthorized entry. These systems, combined with robust cybersecurity measures, are vital for safeguarding patient information.
- Access Control Systems: Hospitals often employ card-based access control systems, restricting access to specific areas based on employee roles and authorization levels. Biometric systems, like fingerprint or facial recognition, further enhance security, reducing unauthorized access.
- Surveillance Systems: Surveillance cameras strategically placed throughout the facility record activity and deter potential threats. Real-time monitoring allows for rapid response to incidents, and recordings serve as evidence in case of security breaches.
- Data Encryption: Healthcare organizations encrypt sensitive patient data both in transit and at rest. Advanced encryption protocols ensure confidentiality and protect against unauthorized access, adhering to regulations like HIPAA.
Security Systems in Finance
Financial institutions face significant risks, including fraud and data breaches. Security measures must be proactive and robust to prevent financial losses and maintain customer trust. A multifaceted approach to security is critical for this industry.
- Transaction Security: Financial institutions use advanced encryption protocols and secure payment gateways to protect transactions during online banking and e-commerce. Two-factor authentication adds another layer of security to access sensitive accounts.
- Fraud Detection Systems: Sophisticated algorithms detect unusual transaction patterns and suspicious activity in real-time, enabling quick responses to potential fraud attempts. These systems often integrate with various data sources to identify anomalies.
- Physical Security Measures: Banks and other financial institutions often have robust physical security systems, such as security guards, surveillance cameras, and alarm systems, to protect their premises from robbery and vandalism. They often utilize reinforced doors and vaults to safeguard cash and valuables.
Security System Layouts for Retail Businesses
Retail environments require comprehensive security systems to safeguard inventory, customers, and employees. Implementing effective layouts is crucial to achieve this.
| Business Type | Security System Layout Example |
|---|---|
| Large Retail Store | Perimeter fencing, security guards, multiple access points with card readers, CCTV cameras strategically placed, and robust alarm systems. |
| Small Boutique | Point of sale security, CCTV cameras covering high-value areas, and a reliable alarm system linked to a security monitoring service. Access control system limiting access to staff only. |
Security Measures to Address Threats in Different Industries
Various threats necessitate tailored security measures. The choice of security systems depends on the specific threats and vulnerabilities.
- Phishing Attacks: Businesses across all sectors must implement cybersecurity training programs to educate employees on identifying phishing emails and other malicious communications. Strong spam filters and email security protocols are essential.
- Data Breaches: Data loss prevention (DLP) tools and strong access controls are vital to prevent sensitive data from falling into the wrong hands. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify vulnerabilities.
Role of Industry Regulations and Standards
Industry regulations and standards play a critical role in security implementations. Compliance with these guidelines is often mandatory for businesses. Examples include HIPAA in healthcare and PCI DSS in finance.
Ending Remarks: Business Security Systems
In conclusion, building a secure business environment requires a multifaceted approach. This overview highlights the importance of physical security, cybersecurity, and data security, while also emphasizing the critical role of integration, management, and ongoing adaptation. By considering cost-benefit analyses and embracing emerging trends, businesses can proactively protect their assets, maintain operational continuity, and foster a thriving future.